The Skin Infection Erysipelas: Problems And Solutions
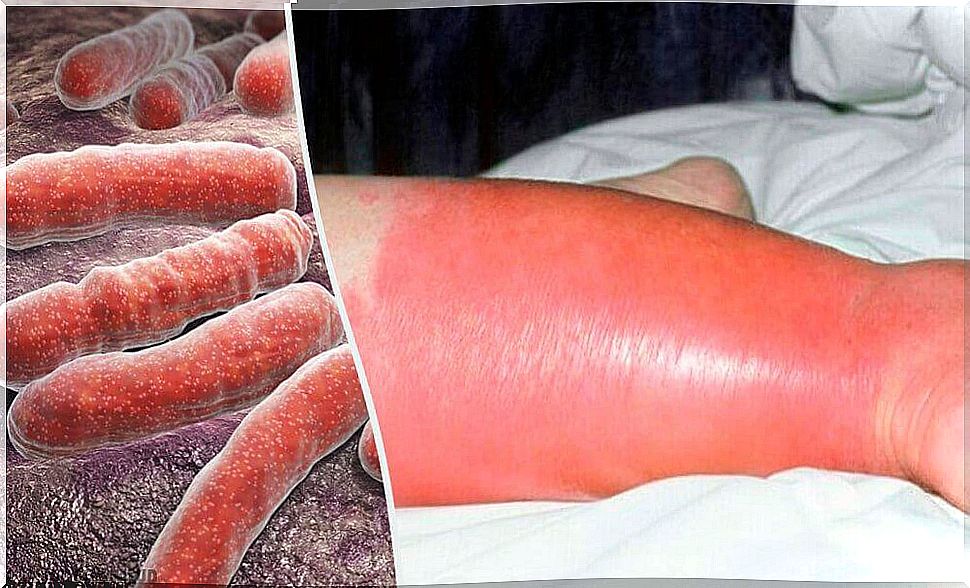
The skin infection erysipelas is a contagious infection. It starts with the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes (Streptococcus) and also the Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus). However, this condition has increased in the last five years. And this is especially true in places where these bacteria are common.
It can also take the form of a cellulite-like infection. At first it appears on the surface. But then it goes deeper into the skin and spreads further.
The first lesion is usually an evolving erythematous papule. It is rapidly increasing in size. It then creates a limitless and very painful erythematous plaque.
The gradual effects of the primary lesion change the skin near the plaques. And it looks like an orange peel. They are also often associated with lymphangitis (inflammation of the lymphatic system) and other systemic symptoms of ill health. But a specialized clinic can treat these symptoms.
Causes of the skin infection erysipelas
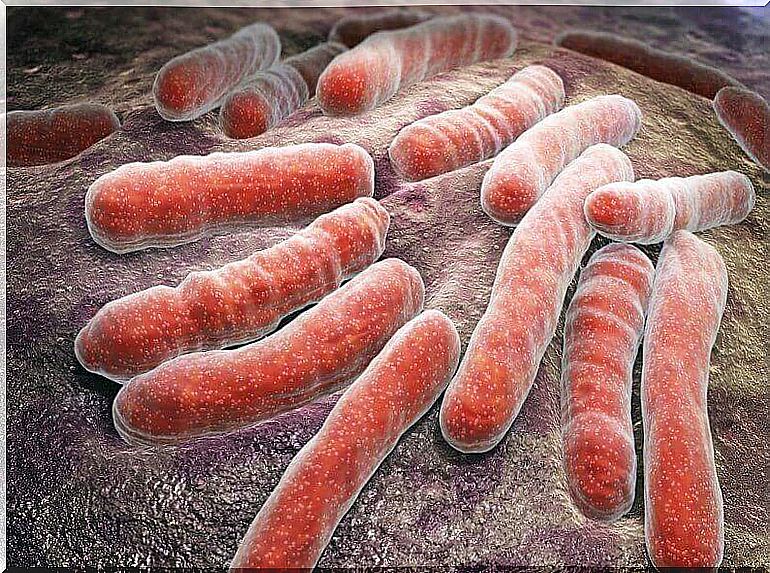
In general, the infection that causes erysipelas is not contagious. However, the direct bacterial origin is Streptococcus and Staphylococcus . The latter is the most common bacteria in skin lesions.
These bacteria also colonize from an entrance in the skin. Basically, this could be an open wound or an inflamed hair follicle. It can also occur through an infected pore. It is also possible that it starts with an insect bite.
However, there are risk factors in every individual. And these factors can also cause the bacteria to colonize the affected area much faster. In general, this is due to the ineffectiveness of the immune system itself. For example, some of these risk factors include:
- nephrotic syndrome
- venous or lymphatic obstruction
- type 2 diabetes mellitus
Symptoms of the skin infection erysipelas
The symptoms are immediately apparent. The local signs of inflammation are clearly visible, which are usually found in the lower extremities and also on the face, which is the preferred target.
Early Signs
- feel warm
- To blush
- Intense pain
- Functional limitation
- Edema in the affected area
More severe symptoms
- Fever
- Weakness
- Lymphangitis
- shivering
- Overall feeling of unease
Complications
- Glomerulonephritis (kidney filter inflammation)
- Thrombophlebitis (superficial vein thrombosis)
- Bacteremia
- Toxic shock
Diagnosis
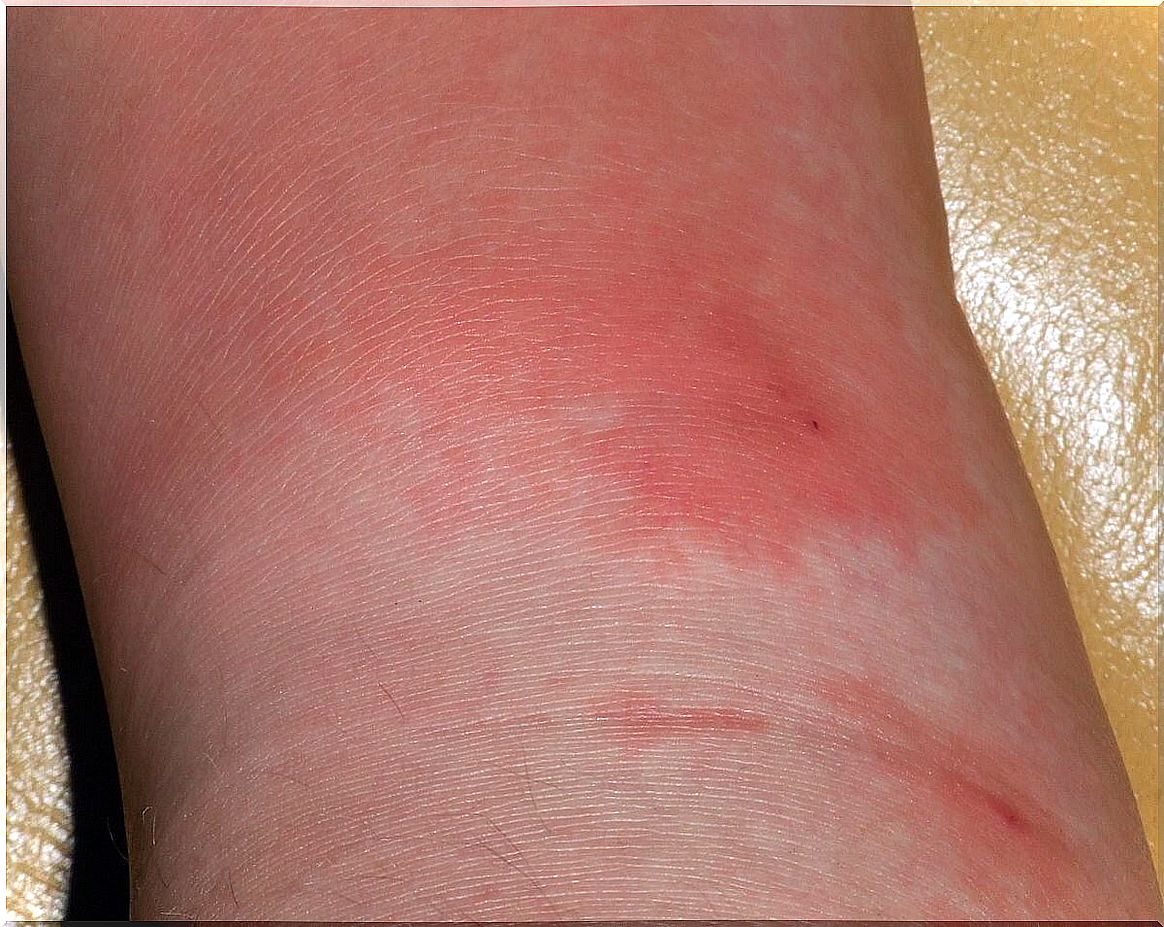
The onset of the skin infection erysipelas is abrupt. And it usually develops quickly. In addition, the thickening of the skin is noticeable in less than 24 hours. Because of this, this condition usually occurs in the lower extremities. The doctor will try to determine a body temperature of more than 38°C or, failing that, chills.
A diagnosis is made on the basis of a physical examination of the patient. And it also includes an interview with the patient and a review of the patient’s clinical history.
Treatment of the skin infection erysipelas
Dandruff cannot be treated with pharmacological treatment alone, as it is an infection that affects both layers of the skin – dermis and epidermis. It is a condition that requires good care and hygiene measures to ensure that the lesion heals properly and the pain may gradually subside until the lesion is completely healed.
Additional care
- Good skin hygiene around the affected area.
- Absolute tranquility of whatever part of your body is affected.
- Elevating the affected body part to reduce edema and also relieve pain.
- Thermotherapy with a cloth soaked in magnesium sulfate to reduce inflammation.
- Remove discharge from open wounds three times a day using sterile dressings hydrated in a physiological solution.
Pharmacological Therapy
First choice drugs
- Oxacillin: 1 – 2 grams intravenously every 4 hours at 6 hours for 10 days.
Pediatric dose: 200 mg/kg/day every 6 hours. - Cephalexin: 500 mg orally every 7 hours for 7 days.
Pediatric dose: 25 mg/kg/day every 6 hours. - Crystalline Penicillin: 4 million IU every 4 hours for 7 days.
second choice drugs
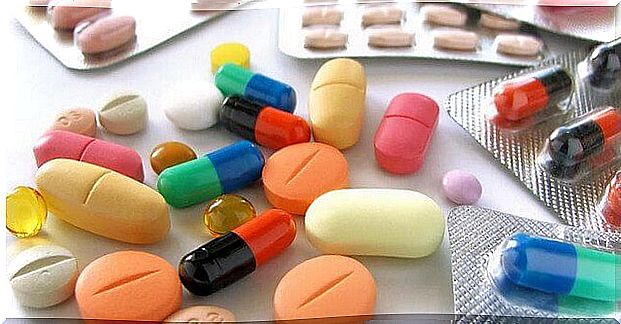
- Ciprofloxacin: 200 mg intravenously every 12 hours for 7 days.
Its administration is not recommended in children under 10 years of age. - Ceftriaxone: 1 gram intravenously once daily for 10 days.
Pediatric dose: 50 – 100 mg/kg/day. - Ampicillin/ Sulbactam: 1.5 – 3 grams intravenously every 6 hours for 7 days.
Pediatric dose: 200 mg/kg/day every 6 hours.
Tablets: 750 mg orally every 12 hours for 7 days.
Recommendation
Patients affected by this condition should switch to oral treatment when the more severe symptoms resolve. They should do this especially if there is no fever and the skin is clearly improving. This usually takes 3 to 5 days, so the improvement will not be immediate.
Also, the total duration of treatment is often a maximum of 10 to 14 days. But as always, this depends on your body’s response.
References
The information in this article is based on this research.