Do’s And Don’ts When Treating A Wound
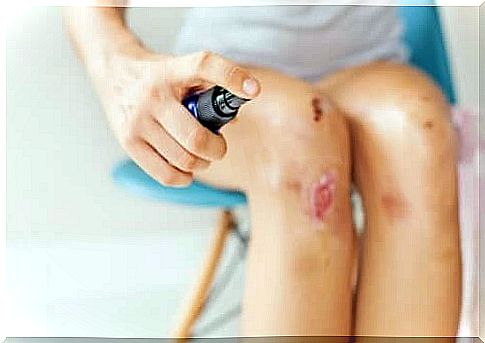
In order for a wound to heal properly and to prevent infections that can lead to other health problems, several factors must be considered. To do the right thing, there are a few things to avoid when treating a wound.
The skin is the largest organ of the human body and it protects the body against viruses, bacteria and fungi. When the skin is damaged, the risk increases that these unwanted elements will penetrate the skin and attack other organs. The deeper, bigger, or dirtier the wound is, the more careful you need to be.
What should you avoid when treating a wound?
When it comes to treating a wound, there are some things to avoid. Applying a tight bandage or tourniquet to stop the bleeding is a serious mistake as it can cause necrosis in the extremities. Do not burn or freeze the wound closed.
Cotton wool or alcohol
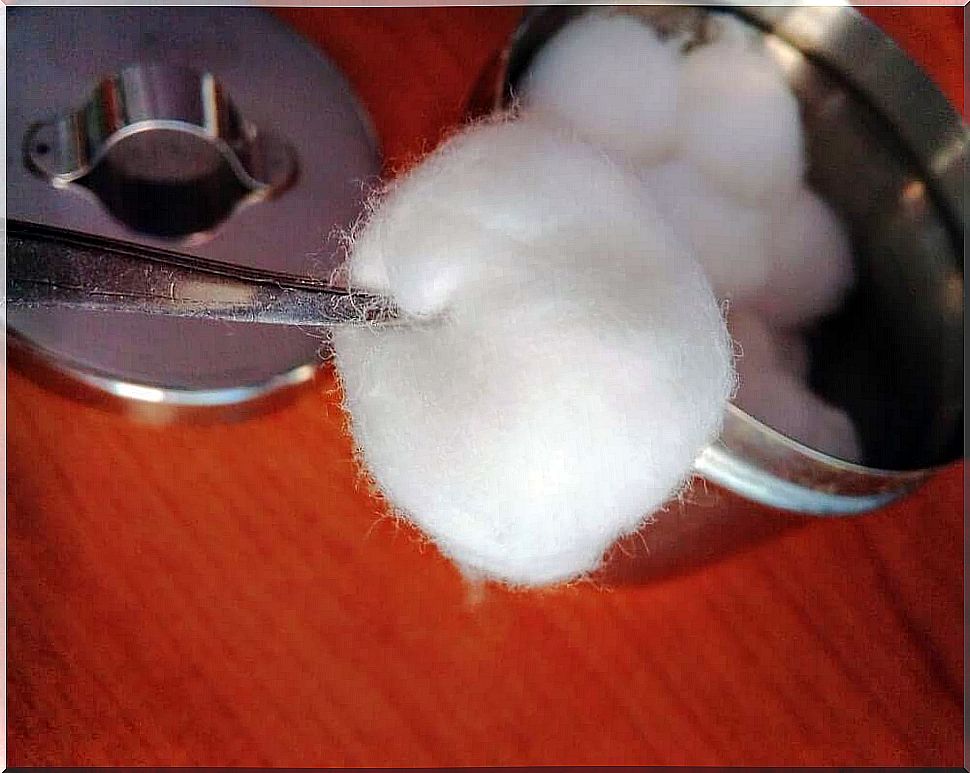

The problem with using cotton wool is that they leave behind fibers that can cause damage if the wound closes with these fibers still in it. It is also not advisable to use alcohol-based products. These agents are irritating and some have vasodilatory effects.
It is best to use special sterile gauzes that do not shed fibers and reduce the risk of cotton wool. In addition, it is better to use antiseptics such as povidone-iodine (Betadine ®) or chlorhexidine solutions.
While both have high antiseptic properties, povidone will not work in the presence of body fluids. Therefore, in case of pus formation or blood, it is better to use chlorhexidine.
Do not rub the wound or remove any particles
Do not rub the wound or remove any foreign objects such as dirt, glass, wood or iron. If these particles are large, they can block the bleeding. So leave this to the doctor.
Do not delay a visit to the doctor, especially if the wound is large and deep. Major wounds caused by humans or animal bites and those caused by sharp objects should be evaluated by the doctor immediately. A tetanus shot may be required.
Recommendations for treating a wound
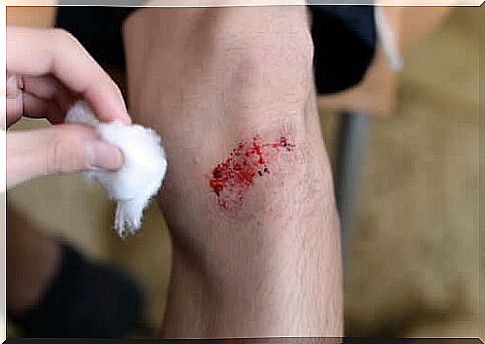
To reduce the risk of infection, follow these steps when treating a small to medium wound:
- First make sure that the person who is going to clean the wound has clean hands. Then clean the wound with tap water, hydrogen peroxide, or saline. Avoid contact with blood to minimize the risk of infection.
- The next thing to do is to dry the surrounding skin without touching the wound. If an antiseptic is available, use it now. Clean the wound in circular motions from the inside out.
- Then cover the wound with sterile gauze and tape or bandage to protect the damaged skin.
- If the wound starts to bleed, stop. With one hand, press a piece of gauze or a clean cloth that does not leave any fibers on the wound. When the bleeding stops, cover the wound with a bandage or bandage.
- Don’t wait more than six hours before seeking medical attention. This will prevent further complications such as poor healing or infections.
Wounds in children
In the case of minor wounds in children, it is advisable to wash them with tap water (running water) to remove the dirt. Using saline or purified water if you have it is even better. You can also use mild soap.
Then dry the wound by dabbing, not rubbing. Make small dabbing movements and work from the inside out. After that, apply an antiseptic and cover the wound with sterile gauze and tape. This process must be repeated periodically. When the scab appears, it is no longer necessary to cover the wound.
If the wound is large and bleeds excessively, hold the body part with the wound up so that it is higher than the heart. Do not use tourniquets on the wound. If clots get into the gauze, leave it in place. If the gauze becomes soaked with blood, place another gauze on top, but do not remove the first gauze.
At first, the wound may be inflamed and red, indicating that the immune system is working to fight off further infection. When the scab appears, it is best to put a protective layer over it while new tissue is developing.
The importance of going to the doctor
It is essential to see a doctor in the following cases:
- If the wound does not stop bleeding or if it starts bleeding again, it is necessary to go to the doctor.
- When there are foreign objects in the wound and especially if they are large, it is also necessary to visit the doctor. Specialists can also treat large, deep wounds.
- A doctor should properly evaluate wounds to the neck, joints, genitals, and face. The first three are functional areas, the face is aesthetic care.
- You urgently need to go to the emergency room when it comes to a wound where a body part has come loose. Bring the detached part in a container with ice.
- If the blood that comes out pulsates, it’s an arterial bleed. This is a very serious case and requires an immediate trip to the hospital.
The above considerations are important when treating a wound. The knowledge and information you have about its treatment can make the difference between successful treatment and the development of complications.